Booster Pump Installation Rules and Key Considerations
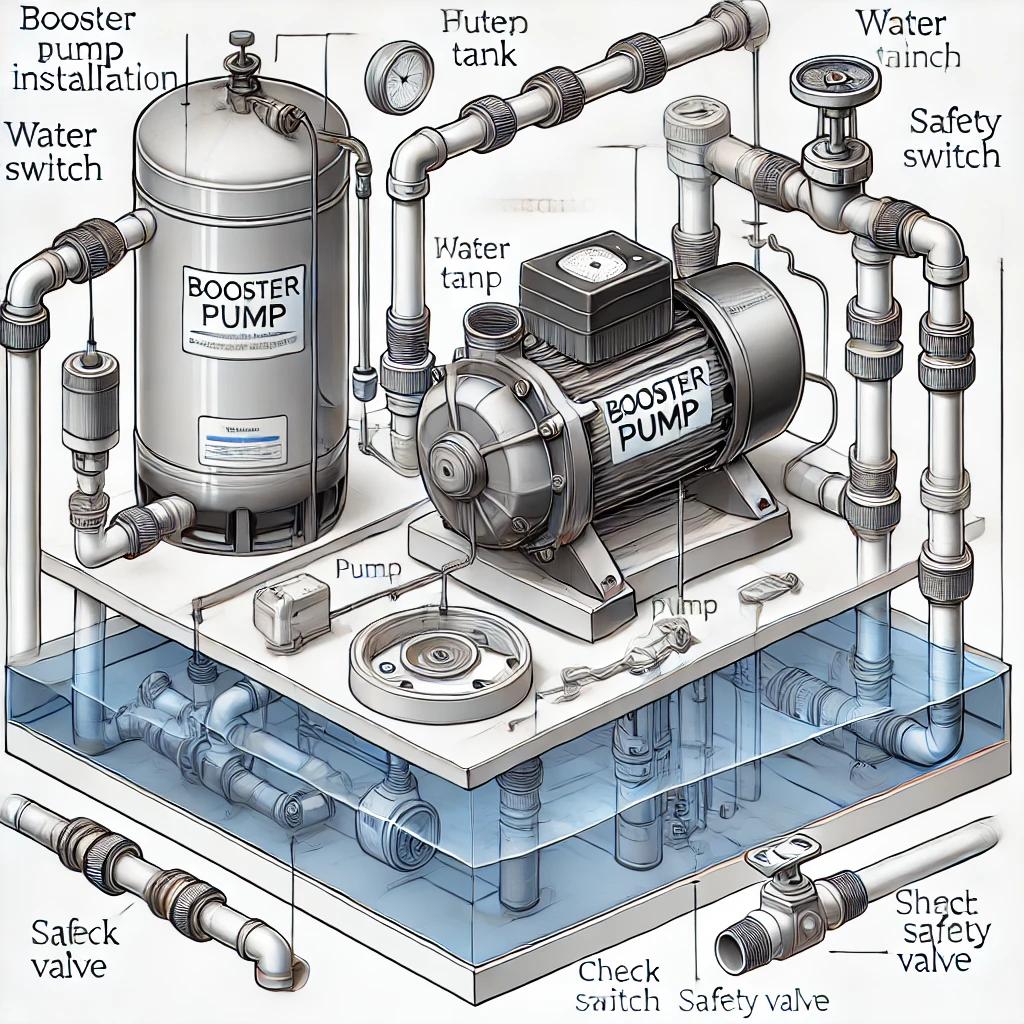
Booster Pump Site Selection
Selecting the right location for a booster pump is crucial for its efficiency and longevity. If the installation site, such as a well or a cistern, exceeds a depth of 7-8 meters, double-suction deep well booster pumps should be used for depths of 12-20 meters.
The pump should be placed away from heat sources like burners and boilers. Additionally, adequate space should be left around the pump for maintenance and repairs.
Booster Pump Water Inlet Installation
To ensure proper water flow and prevent damage, the following rules must be followed:
- The booster pump must be supplied from a water tank and should not be directly connected to the municipal water network.
- The piping should be made of pressure-resistant materials such as galvanized steel, polyethylene, or polypropylene.
- If plastic pipes are used, they must be at least 1 1/2 inches in diameter to avoid internal diameter restrictions.
- A float switch should be installed in the water tank to prevent dry running, which can lead to overheating and mechanical seal failure.
- A filter should be placed on the suction line to prevent debris from entering the pump.
- The distance between the pump and the water tank should be a maximum of 10 meters for optimal performance.
- If water is drawn from a lower-level tank, additional measures should be taken to maintain suction efficiency, as performance may decrease by 10-20%.
Booster Pump Connection Schematics
Compressed Air-Supplied Booster Pump Installation
A compressor is used to pressurize the booster pump tank in this system. To ensure proper operation:
- A float valve is installed at the tank inlet to stop the water flow when full.
- A check valve is used at the inlet and outlet to prevent pressure fluctuations.
- A safety valve is installed on the tank to regulate pressure.
Injector-Supplied Booster Pump Tank Installation
In this system, air is supplied via an injector instead of a compressor. The setup follows the same principles as the compressor system but includes a solenoid valve for pressure regulation.
Automatic Control Elements and Electrical Connections
Automatic control components ensure the smooth operation of the booster pump system:
- Float-Switch Controlled Booster Pump: The float switch monitors water levels and prevents unnecessary pump operation.
- Booster Pump Without Float-Switch: The pump operates independently of water levels and is suitable for areas where water depletion is not a concern.
Commissioning and Adjustment
To ensure proper operation of the booster pump, follow these steps:
- Check the suitability of water and electrical installations.
- Ensure there is enough water in the tank.
- Verify the dry-run protection system is correctly installed.
- Fill the suction line with water to prevent air pockets.
- Manually rotate the pump shaft before initial startup to avoid mechanical blockage.
- Confirm the pump operates within the desired pressure range.
By following these steps, you can ensure the booster pump system runs efficiently and safely.
