What is Distillation? Methods and Applications
Distillation is a method used to separate the components of a liquid. This process is widely applied across industrial sectors, laboratories, and even domestic settings to either purify a liquid or separate components from a liquid mixture. So, what exactly is distillation? How is it done, and what are the methods involved? In this article, we will explore these questions in detail.
What is Distillation?
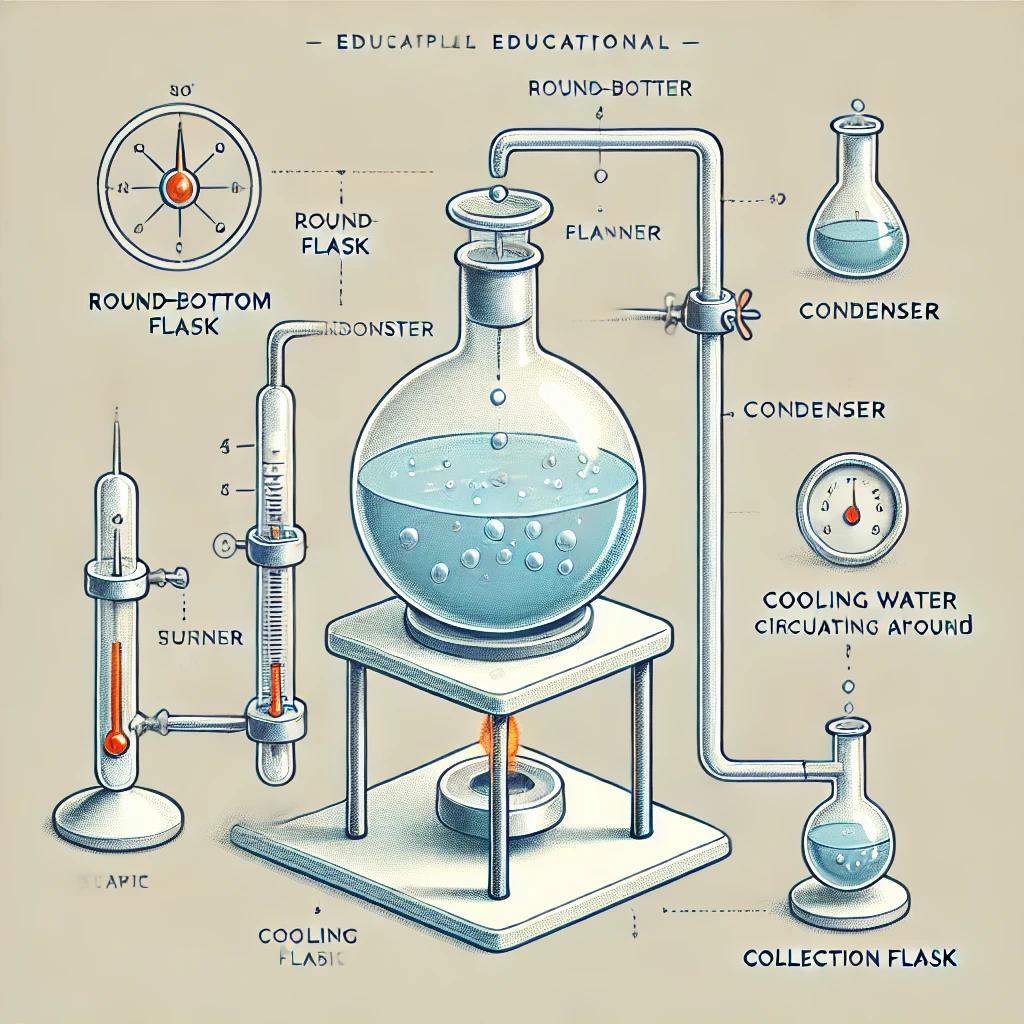
Distillation is the process of separating different components in liquids by vaporizing and then condensing them back into a liquid state. This process takes place in a distillation apparatus where the liquid mixture is heated until it vaporizes. The vapor is then directed onto a cold surface and condensed back into liquid droplets, enabling the separation of components based on their boiling points.
This method is used for various purposes, such as separating liquids from solids, distilling alcohol, refining crude oil into gasoline, kerosene, and lubricating oil, processing chemicals, and desalinating seawater.
Distillation Methods
Distillation processes vary depending on the equipment used and the objectives of the procedure. Common tools include round-bottom flasks, beakers, test tubes, condensers, separating funnels, and membranes. The methods adjust variables like temperature and pressure to suit specific requirements. Here are the most common distillation methods:
1. Simple Distillation
Simple distillation is the most basic method. A liquid is heated until it vaporizes, and the vapor is condensed back into a liquid. This method is ideal for purifying a single liquid.
2. Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation (also known as differential distillation) separates liquid mixtures into components based on their boiling points. Fractionating columns are used, allowing vapors to condense and separate at different levels.
3. Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation reduces the pressure in the apparatus, which lowers the boiling point of the liquid. This is particularly useful for purifying thermally sensitive substances.
4. Steam Distillation
In this method, steam is used to vaporize components instead of direct heating. It is commonly applied for purifying compounds with high boiling points.
5. Rotary Evaporation
Rotary evaporation increases the surface area of a liquid by rotating it in a round-bottom flask, facilitating rapid evaporation. This method is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
6. Fractional Evaporation
Fractional evaporation provides higher levels of purification by boiling and condensing liquids at specific temperatures. It is often preferred for industrial applications requiring high purity.
